In the intricate tapestry of human health, the threads of diet and wellness are interwoven in complex and fascinating ways. Among these, omega-3 fatty acids have emerged as a shining strand, capturing the attention of scientists, nutritionists, and health enthusiasts alike. Known for their myriad health benefits, these essential fats have become the focal point of research exploring their role in reducing inflammation—a silent antagonist in many chronic diseases. As we delve into the science behind omega-3s, we uncover not just their biological mechanisms but also their potential to transform our approach to health and longevity. Join us as we navigate the rich landscape of omega-3s, unraveling how these powerful nutrients can help quell the fires of inflammation and pave the way for a healthier future.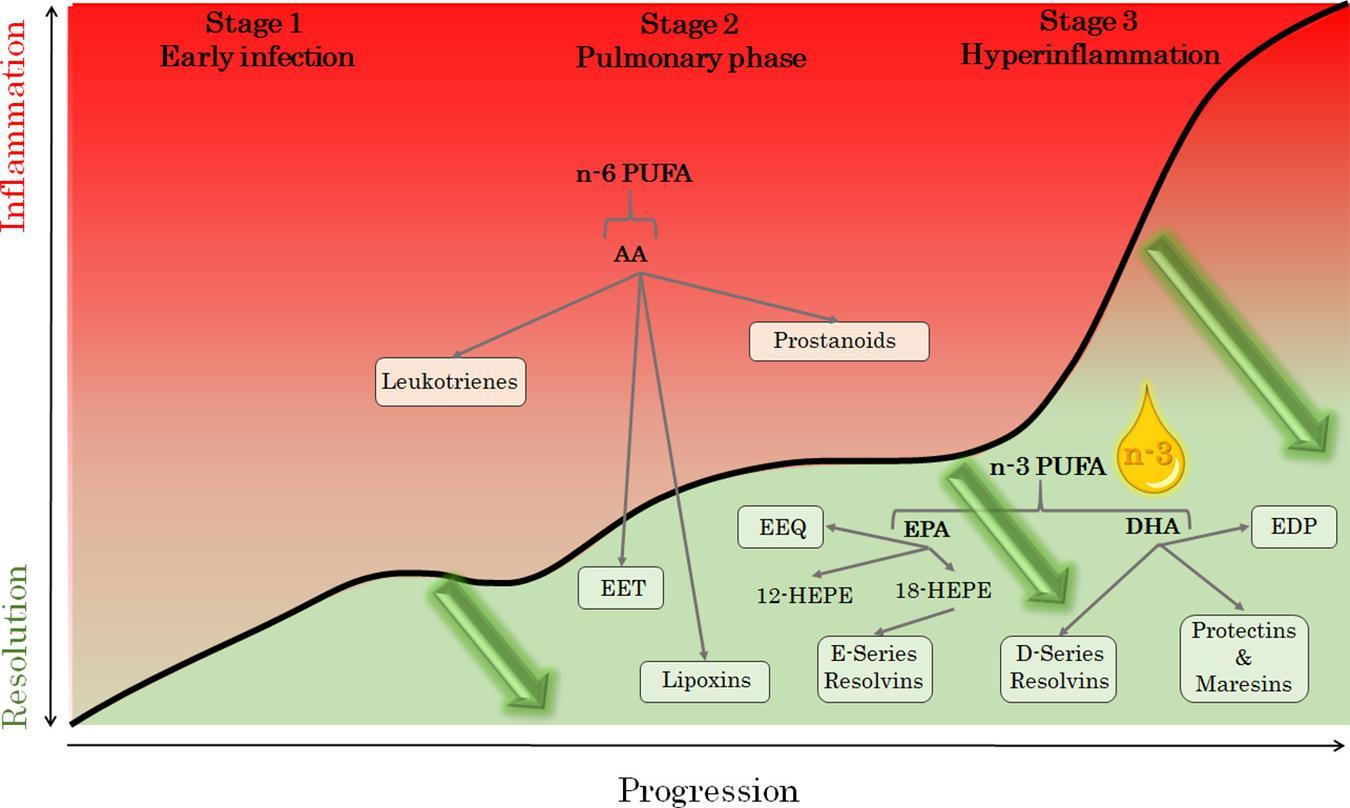
Understanding Omega-3s: Natures Anti-Inflammatory Warriors
Omega-3 fatty acids are lauded for their ability to combat inflammation, a root cause of many chronic diseases. These essential fats, primarily found in fish oil and certain plant oils, work at a cellular level to modulate inflammatory responses. EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are the two most crucial types of omega-3s, known for their powerful anti-inflammatory effects. They function by reducing the production of inflammatory eicosanoids and cytokines, which are the body’s natural signals that can trigger inflammation.
- Reducing Joint Pain: Omega-3s can alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, decreasing joint pain and stiffness.
- Supporting Heart Health: By lowering triglyceride levels and blood pressure, these fatty acids help protect the cardiovascular system.
- Enhancing Brain Function: Omega-3s are vital for maintaining optimal brain health, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds into your diet or considering supplements can be a strategic approach to harnessing these natural anti-inflammatory agents.
Delving into the Science: How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Combat Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids are powerful agents in the fight against inflammation, offering benefits that extend beyond heart health. These essential nutrients, primarily found in fish oils and certain plant oils, interact with cell membranes to influence cellular signaling and gene expression. This interaction results in the production of resolvins and protectins, compounds that actively reduce inflammation. Through their anti-inflammatory prowess, omega-3s can help manage chronic conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and even depression.
- Cell Membrane Integration: Omega-3s become part of cell membranes, enhancing their fluidity and function.
- Anti-inflammatory Molecules: They promote the creation of resolvins and protectins, which directly combat inflammation.
- Gene Expression Modulation: These fatty acids can turn off genes associated with inflammatory responses.
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet or taking supplements can therefore serve as a natural strategy to mitigate inflammation, offering a host of potential health benefits without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical interventions. Whether you choose salmon, flaxseeds, or walnuts, integrating these sources into your daily routine can be a step toward a healthier, more balanced life.

Choosing the Right Sources: Incorporating Omega-3s into Your Diet
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can be a transformative step towards better health, particularly when it comes to managing inflammation. To ensure you’re getting the most out of these essential fats, it’s crucial to select sources that are both rich in omega-3s and fit seamlessly into your lifestyle. Here are some options to consider:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are among the best choices, offering a potent dose of omega-3s. Aim to include these in your meals at least twice a week for maximum benefits.
- Plant-Based Alternatives: For those who prefer a plant-based diet, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are excellent options. Incorporate them into smoothies, salads, or baked goods for a nutritious boost.
- Supplements: When dietary sources are insufficient, omega-3 supplements like fish oil or algae oil can be a convenient option. Be sure to choose high-quality products that are tested for purity.
By diversifying your sources of omega-3s, you can tailor your diet to suit your preferences and nutritional needs while effectively supporting your body’s anti-inflammatory processes.

Expert Tips: Optimizing Omega-3 Intake for Maximum Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
To harness the full potential of omega-3s in combating inflammation, it’s essential to incorporate these fatty acids into your diet strategically. Here are some expert tips to optimize your intake:
- Choose Quality Sources: Opt for wild-caught fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in EPA and DHA, the most potent forms of omega-3s.
- Balance Your Ratios: Ensure your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is balanced. A diet high in processed foods can tip the scale towards omega-6, diminishing omega-3’s anti-inflammatory effects.
- Supplement Wisely: If dietary sources are insufficient, consider supplements. Look for those that are third-party tested for purity and potency.
- Pay Attention to Cooking Methods: Avoid frying omega-3-rich foods as high heat can degrade these delicate fats. Opt for baking, steaming, or grilling instead.
- Incorporate Plant-Based Options: For those who prefer plant-based sources, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts provide ALA, a precursor to EPA and DHA, though conversion rates can vary.

